RDS
- It’s a managed SQL database service. (related: SQL vs NoSQL), so it’s less complicated than manually configuring an EC2, for example
- It handles daily or automated backups, patching, and you can enable multi-AZ for high availability
- You can create multiple dbs & multiple db engines
- They are db software running on top of EC2 instances under the hood
- An RDS instance is like an EC2 instance that is specifically designed to run a database
- A regional service
Configuration
- diagram
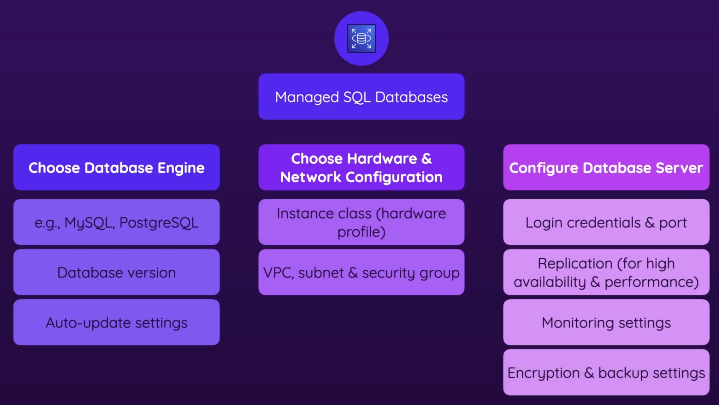
- choose an engine
- You create a new db by choosing an engine (ex. MySQL, PostgreSQL)
- One of the options is Aurora
- choose version of the engine
- settings (ex. whether you want to automatically update to newer versions)
- You create a new db by choosing an engine (ex. MySQL, PostgreSQL)
- choose hardware & network configuration
- Instance class (hardware profile), kind of like choosing a hardware profile for an EC2 instance
- Choose a VPC, subnet, security group to attach to the db
- configure db server
- login credentials, port
- Replication settings
- monitoring settings to get insights
Aurora
- diagram
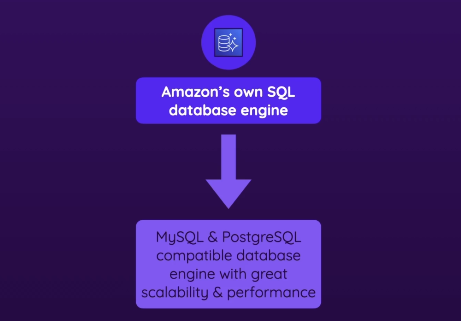
- It is a SQL engine created by Amazon for AWS, with many built in optimizations
- Compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL
- Has lots of great features built in
- Not an engine you can install on your local PC
- Can be a great choice for a relational database, an alternative to MySQL and PostgreSQL
- NOT part of the free tier (can easily get quite expensive)
- Aurora Standard VS Aurora Serverless
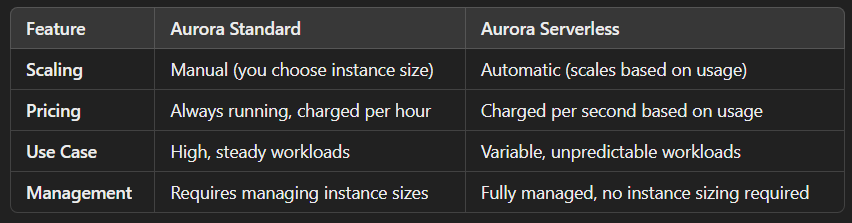
- Aurora Standard
- the default, more often
- Aurora Serverless
- removes the need to manage database servers manually
- automatically scales and pauses when not in use, making it cost-effective for variable workloads.
- near-zero cost when idle
- less features than the non-serverless version
- Serverless feature is only available for Aurora
- Aurora Standard
Pricing based on engines
- RDS with Standard Engines (Fixed Payment)
- Engines: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, SQL Server, Oracle
- Pricing: Charged per hour (whether used or not)
- Think of it like renting a dedicated database server
- RDS with Aurora (Two Pricing Models)
- Aurora Standard: Charged per hour (like regular RDS)
- Aurora Serverless: Pay-as-you-go, billed per second based on usage
Replication settings
- diagram
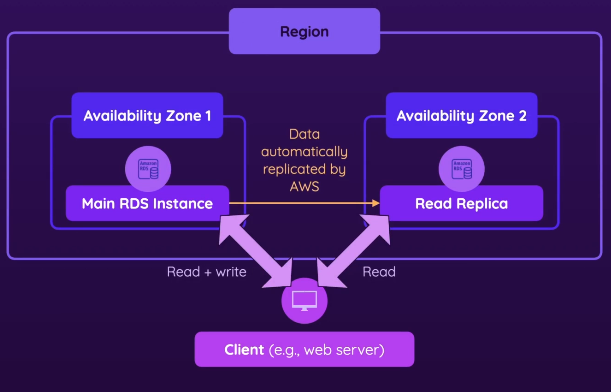
- RDS supports Multi-AZ deployments for high availability.
- AWS can replicate your database to another AZ for redundancy.
- If the primary database fails, AWS automatically switches to the standby in another AZ.
- Useful to make backup instances
- Kind of like S3’s replication feature