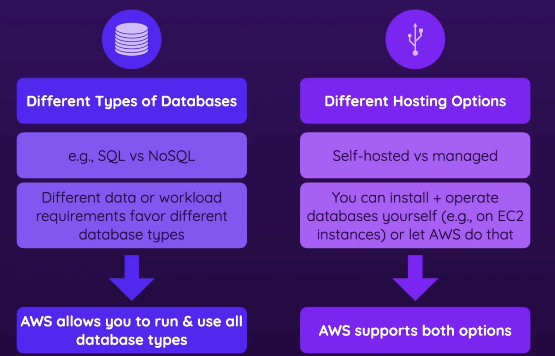
Self-hosted vs Managed
- diagram
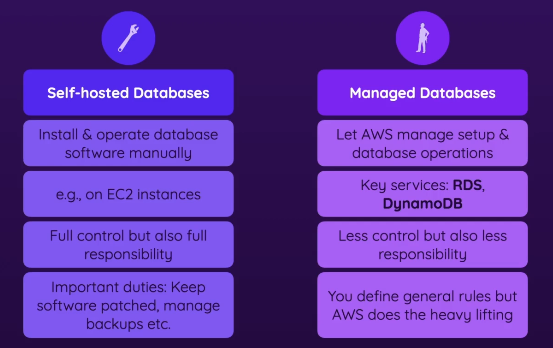
Self-hosted
- Install/manage/operate the db on your own + full responsibility
- You could manage the db on a EC2 Instance
- Maybe you have experts in house, maybe you don’t want to switch
Managed
- Let AWS do the heavy lifting, reduces complexity
- less control & responsibility
- Relational
- Non relational
- Payment for Managed services
- Most AWS managed databases use a fixed pricing model:
- Think of it like renting a dedicated server—you pay for the instance even if you don’t use it (e.g., RDS + most engines).
- Exception: Serverless Databases (Pay-as-you-go)
Relational Databases & VPCs
- diagram - a typical setup
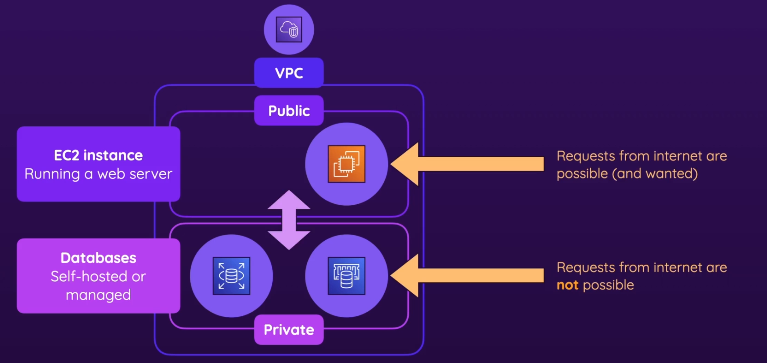
- For RDS (Relational Databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Aurora, etc.)
- You must choose a VPC when creating an RDS database.
- RDS instances are like EC2 instances—they run in a VPC with subnets and Security groups.
- Dbs are usually placed in private subnets, they would be protected from internet access
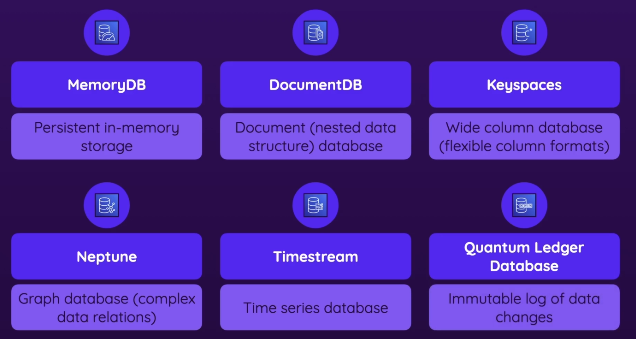
Caching Databases
Non-relational database
AWS Backup
- diagram
- Backups are important for dbs
- Ex. RDS replication settings
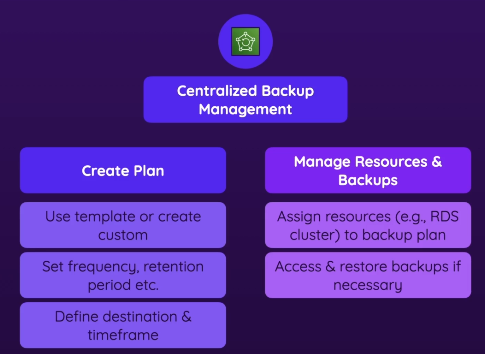
- While RDS has its own built-in backup options, AWS Backup provides a higher-level centralized backup management
- Centralized backup management
- You can view/control your backups in a central way
- Allows you to create a backup plan
- backup frequency, retention period, etc
- Once plan is created