Systems
A service that helps you manage large scale server fleets & application running on top of servers and other compute resources
- a huge service with many capabilities built for complex compute architectures
- Manages & automates AWS resources
- Infrastructure management, patching, automation
Motivation
- What if you’re not just running some batch jobs, but running a large system with 100s or 1000s of servers, maybe even a combinations of servers in the cloud AND in data centers (on-premises)?
- Example Use Cases:
Main Capabilities
- diagram
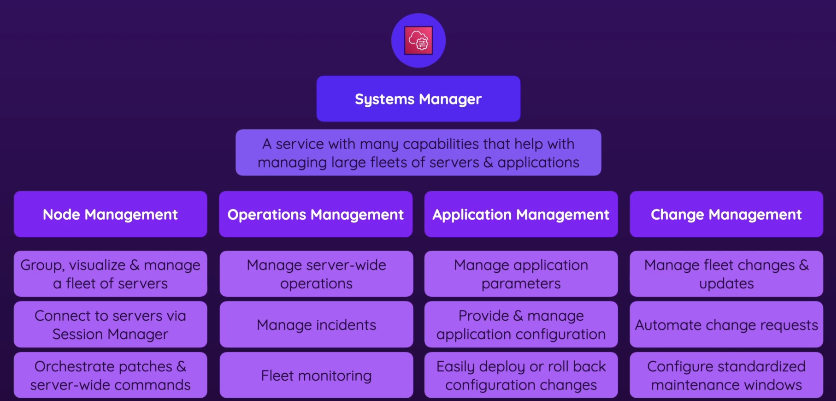
- Node management
- Manages individual nodes (servers)
- Helps visualize, group, and manage the fleet of servers
- allows to connect to different servers via session manager
- servers include the ones in your local data center!
- session manager - one of the connection options you see when you try to connect to an EC2 instance
- Allows you to orchestrate patches and server-wide commands & apply patches to multiple servers at once
- Operations management
- Help with day to day operations
- manage incidents, so if problems arise you can solve it from there
- fleet monitoring
- even set up automation, so you have certain solutions for certain problems when they arise
- Application Management - Parameter store & App Config
- manage application parameters in one central place
- it’s common that the code that makes an app needs certain params (ex. username of user who wants to connect)
- if a value changes, you can use a parameters store
- the the application can automatically reach to this and get the data from there
- AppConfig
- manage application wide configuration - you can set certain values which can be pushed into the app code, without redeploying
- manage application parameters in one central place
- Change management
- Makes fleet changes & updates EASY
- allows automating change requests
Parameter store
- Basically a secure place to store configuration values that your applications need, like:
- Instead of “hard-coding” these values directly in your application code, you store them in Parameter Store
- When using Parameter Store, application code has to actively query that service to fetch a certain value from it
AppConfig
- essentially builds on Parameter Store by adding a push-based configuration system
- You can store values with it, too - but you can then also publish new versions and have your application code use those values automatically.