Ops in MLOps comes from DevOps, short for Developments and Operations. To operationalize something means to bring it into production, which includes deploying, monitoring, and maintaining it. MLOps is a set of tools and best practices for bringing ML into production.
Considerations
The Process
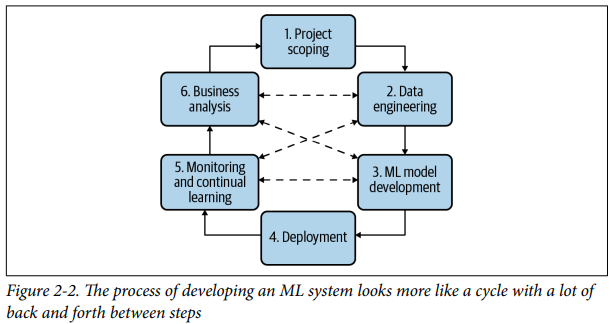
- After the initial deployment, maintenance will often mean going back to perform more error analysis and maybe retrain the model, or it might mean taking the data you get back.
- Now that the system is deployed and is running on live data, and feeding that back into your dataset to then potentially update your data, retrain the model, and so on until you can put an updated model into deployment.
- Example (절망편)
- Choose a metric to optimize. For example, you might want to optimize for impressions—the number of times an ad is shown.
- Collect data and obtain labels.
- Engineer features.
- Train models.
- During error analysis, you realize that errors are caused by the wrong labels, so you relabel the data.
- Train the model again.
- During error analysis, you realize that your model always predicts that an ad shouldn’t be shown, and the reason is because 99.99% of the data you have have NEGATIVE labels (ads that shouldn’t be shown). So you have to collect more data of ads that should be shown.
- Train the model again.
- The model performs well on your existing test data, which is by now two months old. However, it performs poorly on the data from yesterday. Your model is now stale, so you need to update it on more recent data.
- Train the model again.
- Deploy the model.
- The model seems to be performing well, but then the businesspeople come knocking on your door asking why the revenue is decreasing. It turns out the ads are being shown, but few people click on them. So you want to change your model to optimize for ad click-through rate instead.
- Go to step 1.
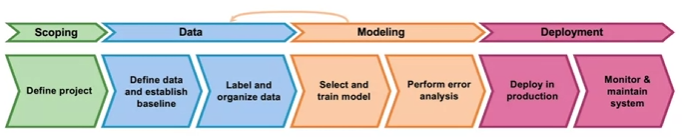
Steps
- Scoping
- Data Engineering
- ML model development
- Deployment
- Monitoring and continual learning
- Business analysis
- Some challenges
- Concept drift/data drift
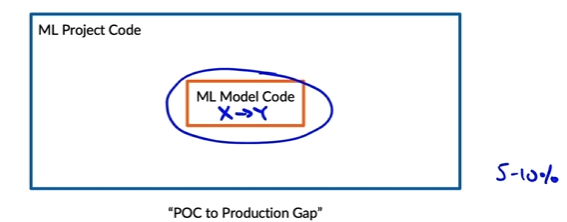
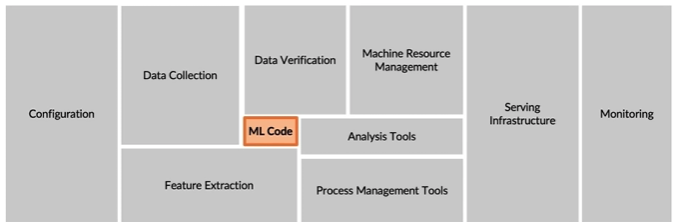
- Just mode than machine learning code
- The requirements surrounding ML infrastructure
Sources
- Designing Machine Learning Systems book: https://drive.google.com/file/d/13dmlGavqr5XtZijQuwfcHAc7cY4k4-l8/view?pli=1
- Andrew Ng’s Machine Learning in Production Course