The implications ML can solve
- The system has capacity to learn patterns (often complex)
- Not useful when you can just look up through a relational database, but useful when there is potential to actually learn, like predicting Airbnb pricings from characteristics (date, size, etc)
- You have to let the ML system figure out the pattern
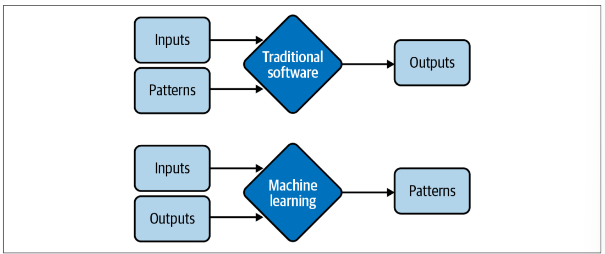
- There is existing data / It’s possible to collect data
- Sometimes ML models are deployed without having been trained so that they will learn from incoming data in production. This is risky. (Fake it till make it)
- Solving problems that require predictive answers
- Unseen data
- Your unseen data and training data should come from similar distributions.
Additional good-to-have
- Repetition
- When a pattern is repeated multiple times, it’s easier for machines to learn from it
- The cost of wrong predictions is cheap
- If the ML model recommends an item the user isn’t interested in, the user simply won’t click it. But if the ML model makes a wrong move in an autonomous vehicle, it’s deadly (but it’s still wildly being developed since the good - if achieved - outweighs the bad significantly)
- It’s at scale
- Making LOTS of predictions (ex. include sorting through millions of emails a year or predicting which departments thousands of support tickets should be routed to a day. )
- Having a problem at scale also means that there’s a lot of data for you to collect, which is useful for training ML models.
- Constantly changing patterns
- You can’t code/handwrite every single rule to the changing pattern, let your ML model learn from it!
Cases in real life
ML systems serve both internal and external
- Internal: reducing costs, generating customer insight, internal processing automation
- External: improving customer experience, customer interaction
- Fraud detection
- Price optimization
- Churn prediction (predicting when a specific customer is about to stop using your products or services so that you can take appropriate actions to win them back)
- Brand monitoring (monitoring how the public/customers view your brand)
Example (from Andrew Ng’s course)
- In a phone factory, there may be an edge device (Device living inside a factory that manufactures the smartphones) which has an inspection software that detects if there is a scratch. It controls a camera which takes picture, then passes the picture to a prediction server which returns
- You will put the CV model you made in the prediction server, set API interfaces, and write software to deploy this DL algorithm into production