“Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed” - Arthur Samuel (1959)
- In general the more data the algorithm learns from, the better the result
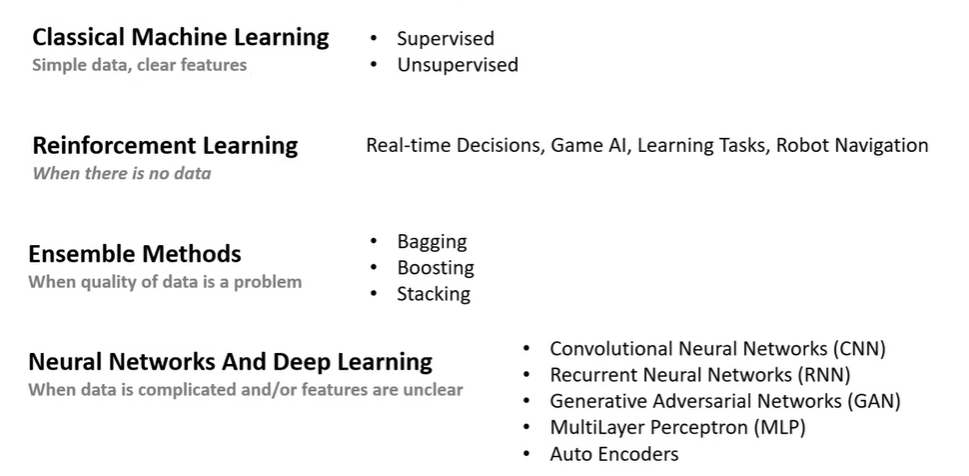
- Types of ML algorithms based on what problem they solve
- Supervised learning
- Unsupervised learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Hybrid learning problems
- semi-supervised
- training data contains very few labeled examples and a large number of unlabeled examples
- self-supervised
- framed as a supervised learning problem in order to apply supervised learning algorithms
- multi-instance
- individual examples are unlabeled, instead, bags or groups of samples are labeled
- semi-supervised
Divisions of ml
Supervised learning
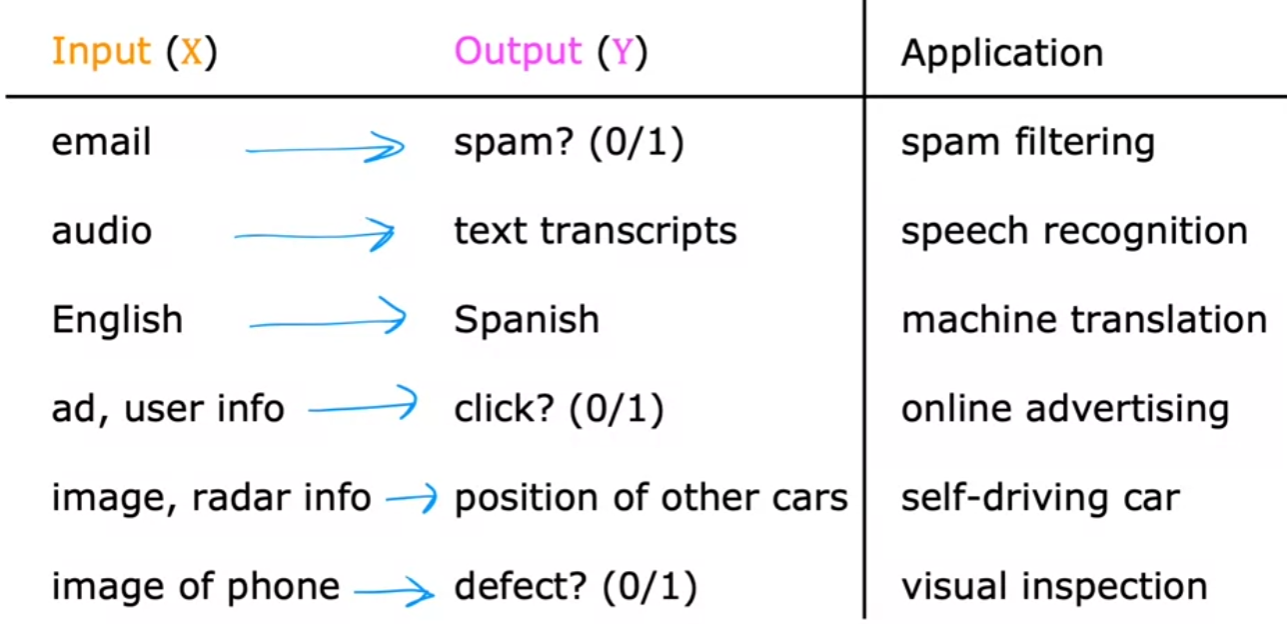
Algorithms that learn
input x -> output y (label)mappings
- A ml task/function that needs to be provided training data (labeled data (correct answer)) and machine can learn from these results
- You give the learning algorithm examples to learn from that includes the “right” answers
- Notation
- Training data: Data used to train the model, has both input and output
- (
x_train): “input” variable, feature - (
y_train): “output” variable, “target” variable (training example targets) - : total number of training examples
- : single training example (ex. means )
- : th training example (
x_i, y_i)
- (
- Model/function
- Estimate/prediction
- Parameters: the variables you can adjust during training to improve the model
- : parameter - weight
- : parameter - bias
- Training data: Data used to train the model, has both input and output
- Real world application
- First train your model w/ examples
input xand the right answerslabels y
- First train your model w/ examples
- Main types of supervised learning
Unsupervised learning
Using a model to describe or extract relationships in data
- A ml task/function that needs NO existing training data
- Data only comes in with inputs
xbut not output labelsy - Our task is NOT getting an output (ex. identifying if the tumor is benign or malignant)
- It automatically figures out the STRUCTURE / PATTERN in the data!
- Main types of supervised learning
- Clustering
- Anomaly Detection
- Dimensionality Reduction
- Association
Reinforcement learning
There is no data, there is an environment and an ML model that generates data and attempts until it reaches a goal
- an agent operates in an environment and must learn to operate using feedback