Lambda
Most popular serverless compute service in AWS (maybe also in the world)
- About executing code in reaction to a certain event
- can have multiple events
- can configure various aspects about this execution
- a regional service
- related: EC2 VS Lambda
Closer Look
- diagram
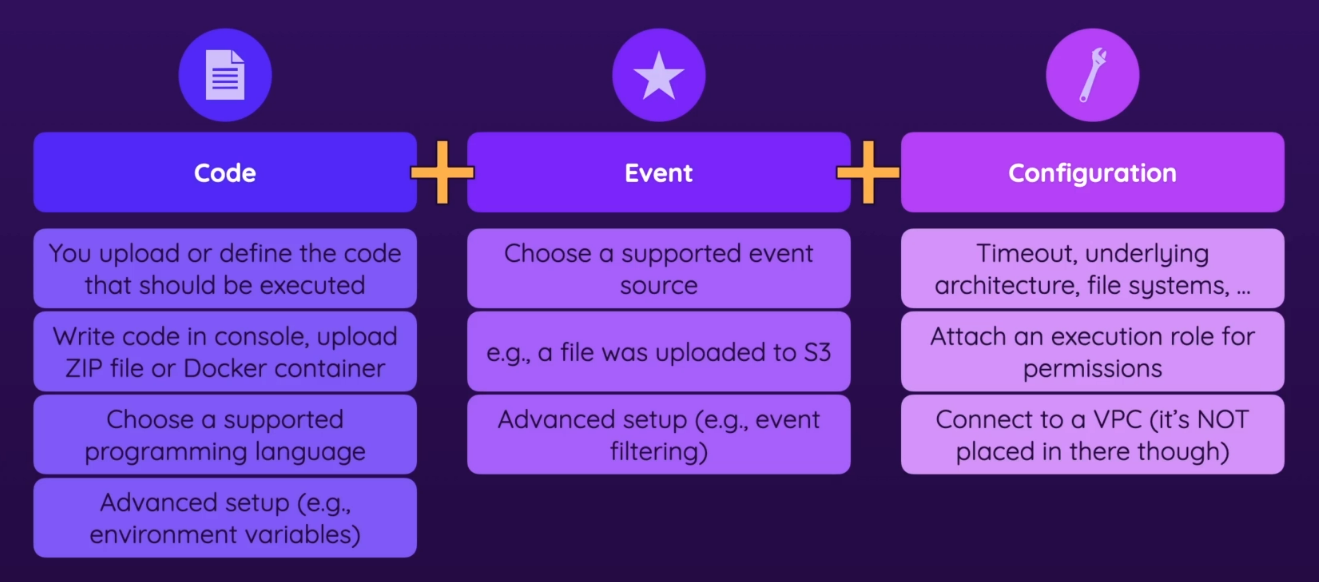
Code
- functions
- the things that contain your code
- when you create a function (when making a lambda instance) you can create one or choose a pre-provided one
- you can upload the code (zip file, docker file) or define (write) the code in the Lambda management console
- choose supported programming language (in theory lambda supports all languages)
- advanced setup (ex. environment variables)
- ex. Node.js
Event
- Choose one of the many supported event sources (ex. file was uploaded to S3)
- there is a broad variety
- filtering - certain variations of a given event (ex. choosing only
.jpgfor event when file is uploaded to S3)
Configuration
- timeout, like how long the code might run at most
- you pay for the time your code is being executed
- choose architecture -
x86_64orarm64 - attach EFS (Elastic File System) as needed
- Attach an execution role for permissions
- the code executed can have certain permissions
- You can connect your lambda function to a VPC
- you can give ur code access to a VPC in case it needs more communication
- configure the memory that should be available
- will impact the pricing
Example
- You could create a new Lambda and create event to S3 bucket
- Give your function the appropriate permissions to access the bucket
- Then you could have code that extracts data from the bucket when event is triggered
Monitoring
- in a function u create, u also have monitoring capabilities enabled out of the box → uses CloudWatch behind the scenes
- In configuration options, you can even enable extra monitoring, like XRay
- related: Monitoring workloads