EBS
A scalable block storage service provided by AWS for EC2 instances
- Allows to attach virtual hard drives to EC2 instances
- Focuses on EC2 instances only and you can’t use with other services
- It is a regional service, so the region you select (on top right) matters
- Volumes are created in specific regions, and can be attached to EC2 instances of the same regions
- EBS volumes are part of free tier, but it is limited
- AWS automatically creates an EBS volume (let’s say 30GB).
- Whilst the root volume typically is deleted together with the instance, other volumes survive instance termination unless configured otherwise
- Resources
With EC2 instances
- diagram
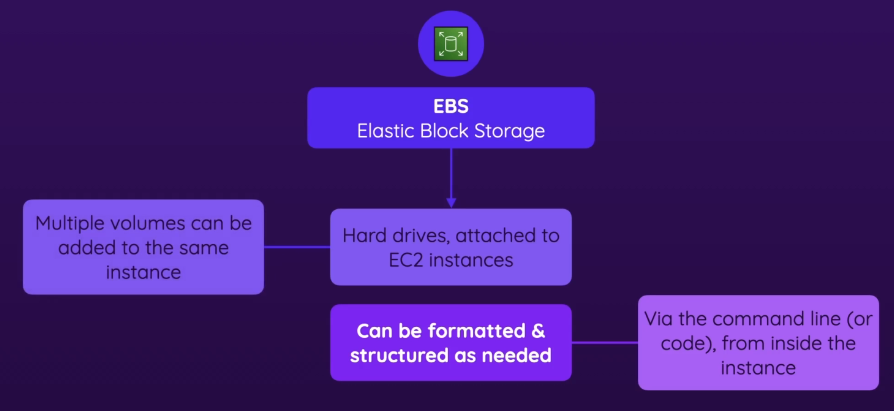
- When you launch an EC2 instance, you can automatically add EBS volumes to that instance
- you can add multiple volumes, give those a name, and choose the kind, size, etc
- Once the instance starts, you have to structure each volume manually
- New volumes are raw storage → They don’t have a file system yet.
- You must format them → Just like adding a new hard drive to a computer.
- You must mount them → So the OS can recognize and use the storage.
- Can be formatted and structured as needed
- with AWS CLI from in the instance
- so you can connect to your instance with SSH → mount & format your hard drive
EBS Core Features
- diagram

- Different types of hard drives you can choose
- You can find a perfect hard drive for your specific workload
- Elastic volumes
- you can scale the volumes as needed, instead of adding an extra volume!
- you can scale dynamically (automatically)
- extra feature that should be managed
- Snapshots
- You can save a snapshot of a EC2 instance and save that snapshot on an EBS volume, then restore that instance/data for a future instance you’re launching
- useful to make sure you’re not losing your data as you terminate your EC2 instance
- reminds me of creating snapshots for linux
- Multi-Attach
- By default when you create an EBS volume, you attach to a single EC2 instance
- Multiple instances might be working on the same kind of task, and might need to access the same files
- Only supported by some instance types
- tricky to set up → resolve file conflicts
EC2 Instance storage
A special term separate from EBS
- diagram
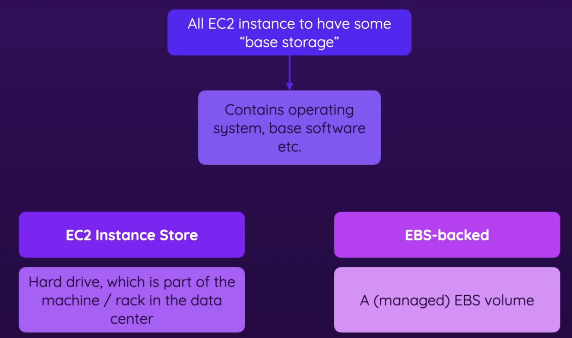
- All EC2 instances have base storage
- EC2 Instance Store
- non-EBS backed storage
- hard drive, part of the machine/rack in the data center
- data is lost if the instance stops or is terminated
- less common
- EBS-backed
- AWS automatically creates an EBS volume (let’s say 30GB) when you launch an EC2 instance
- data persists even if the instance stops
- most common, the default option