- diagram
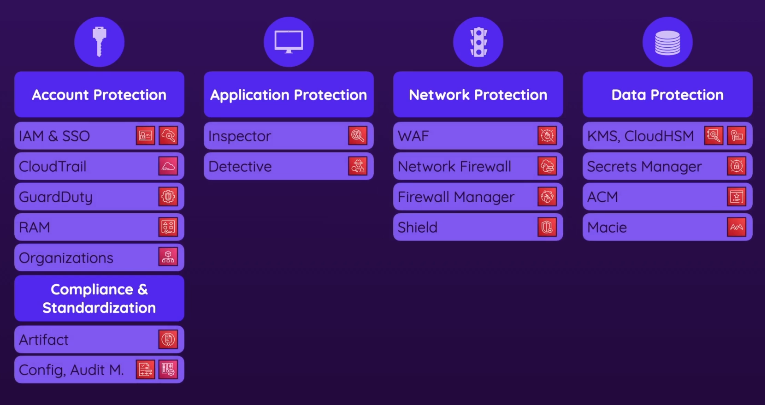
- Account protection
- Account shouldn’t get compromised (secure credentials, multi factor credentials, using IAM users)
- Prevent malicious account / service usage
- Secure cross-account service usage (big companies often use multiple accounts, and they should work together in a secure way)
- Compliance & Standardization
- Single Sign-On (ppl can use same credentials for different things), service config (ppl must follow some guideline/standard), compliance reports
- Application protection
- Detect app/software vulnerabilities
- Detect insecure configurations
- Investigate security issues & incidents
- Network protection
- Detect malicious network traffic (before it arrives in your applications)
- Protect against DDoS attacks
- Data protection
- Encrypt data at rest & in transit
- both when it’s flowing through the network or stored
- Protect code secrets
- In code you use values (and not hard code)
- Prevent unintended data exposure
- Encrypt data at rest & in transit
Account protection
- Permissions & Access Control (IAM)
- Single Sign-On & Active Directory - accessing other accounts easily w/ 1 account
- CloudTrail & GuardDuty - Prevent Malicious Usage
- RAM (Resource Access Manager)
Compliance & Legal requirements
- AWS Config - ensure compliances & best practices
- AWS Artifacts- prove AWS compliance
- Audit Manager- prove your compliance
Application protection
Network protection
- Firewall Manager
- Security groups - instance level
- Network Access Control Lists (NACLs) - subnets level
- WAF (Web App Firewall) - blocks web-based attacks based on content (webapp)
- Network Firewall - blocks threats by filtering network traffic (vpc)
- Shield - avoids DDoS attacks
Data protection
- Security Hub
- data at rest
- data in transit
- Secret Manager - manages sensitive information
- Macie - discover data protection issues in storage