What
- A mechanism that redirects the standard output (
stdout) of one command into the standard input (stdin) of another command- So you can chain multiple commands together and build more complex functionalities
- General syntax:
command | command | .... | command
- Motivation
- Without pipes, how do we count the number of files in a directory?
ls > output.txt,wc -l output.txt,rm output.txt- the
output.txtshould be in a different folder becauselswill count it too - Use pipes, it makes your life easier by allowing you to combine multiple programs together
- no need for temporary file
- Pipe diagram
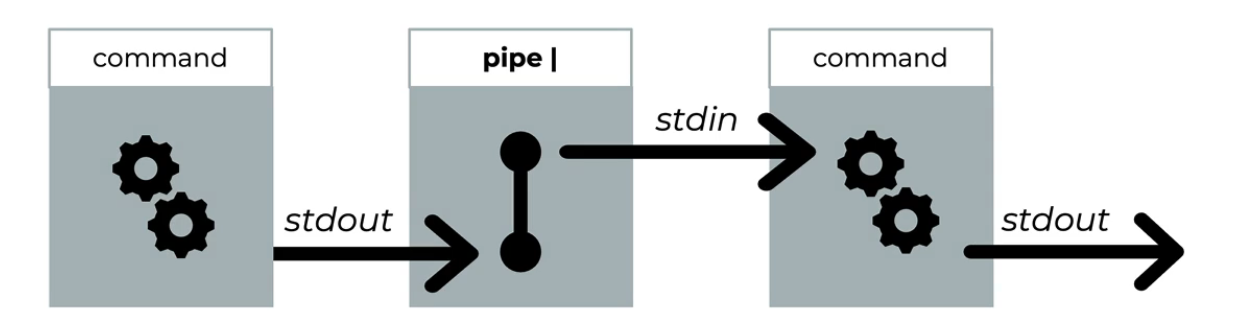
Examples
Example 1
ls | wc -l- ls prints the files to
stdout, then the pipe redirects thestdoutis redirected to thestdinto the 2nd programwc -l. Then the result will be printed ls | catwc -landcatcan also read fromstdin- related: What about stdin
Example 2
leejun@leejun-VirtualBox:~/Desktop$ du -h text.txt not-exist.txt 2>&1 >/dev/null
du: cannot access 'not-exist.txt': No such file or directory
leejun@leejun-VirtualBox:~/Desktop$ du -h text.txt not-exist.txt 2>&1 > /dev/null | wc -l
1- 1st command - redirects error to current
stdout(terminal) then redirectsstdoutto/dev/null - 2nd command - you can use this to count the number of errors
> /dev/null→ Discardsstdout, butstderris still printed to the terminal (as it was redirected to previous currentstdout(terminal)).- the pipe receives this
stderrinput forwc -l - You’re not piping from
/dev/null—you redirected onlystdoutthere. The remainingstderroutput is still available for piping.
Common programs to use with |
tee
- With
|and theteecommand, you can create astdoutand write it to a file at the SAME time! - Example
echo 'Hello Bash' | tee hello.txt- You want
Hello Bashto be printed tostdoutand also written intohello.txt
- You want
echo 'Hello Bash' | tee hello.txt | wc -c- multiple pipes
- counting the text
- Appending
echo 'Hello Bash' | tee -a hello.txt
ping
- Allows us to send a ping packet to another server (ex. a remote server).
- Related: Backend Explained - Servers
- We can use to test if our connection is reachable or disrupted
- Example
ping google.com- sends a ping packet to
google.com
- sends a ping packet to
ping non_existing.com 2>&1 | tee ping.txt- Redirects
stderr (2)tostdout (1), so both error messages and normal output are now part ofstdout. - The
teecommand takesstdinand writes it to both terminal (stdout) andping.txt
- Redirects