Catalogues the web page into individual objects that we can select and manipulate
What is DOM
- the task of converting an html into the DOM is done by the browser when you load up the webpage
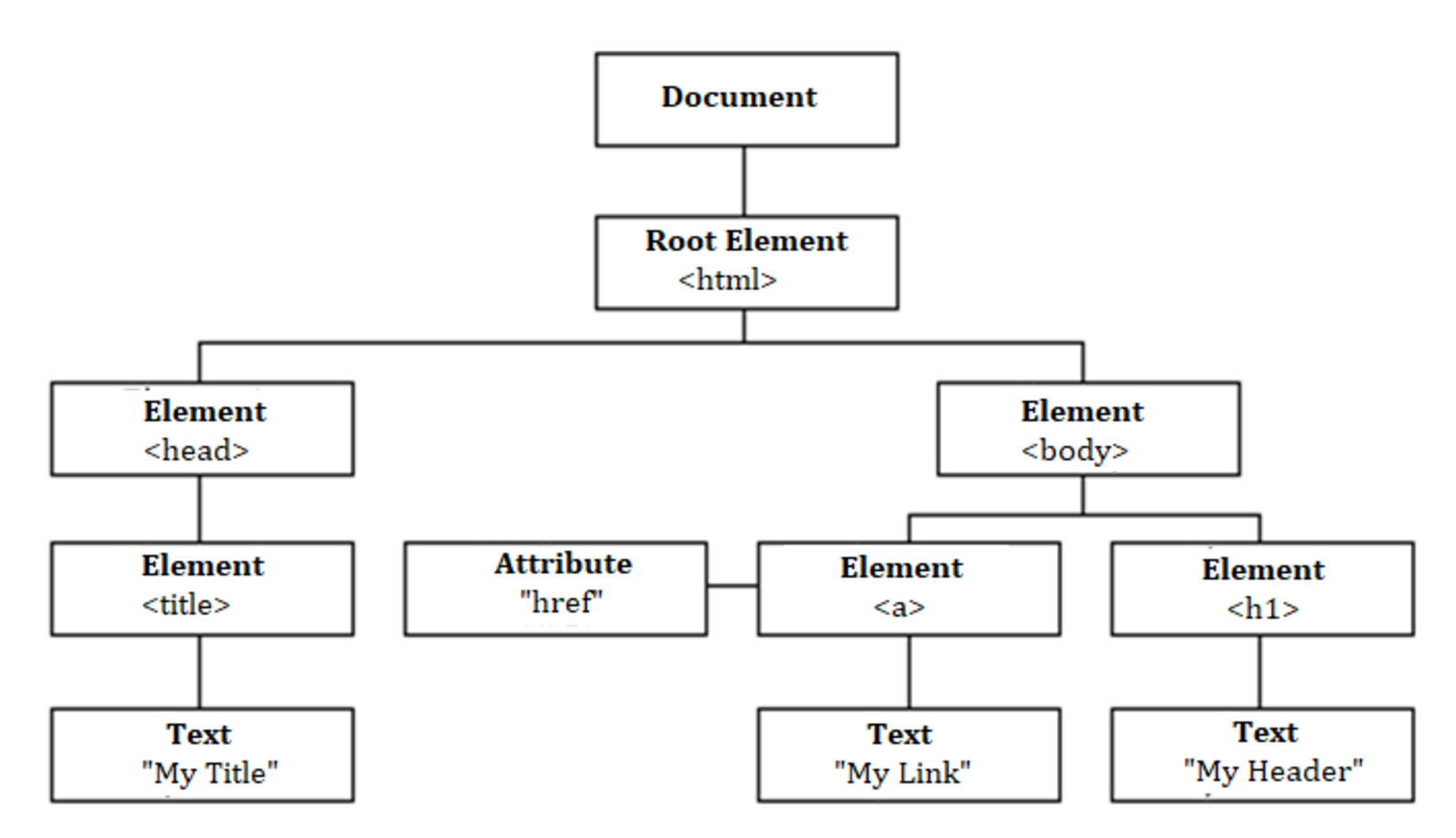
- tree-like representation of the web that gets loaded in the browser
- represents the document as nodes and objects
- when web browser loads an HTML document:
- constructs the DOM and structures all elements in a tree-like representation
- JavaScript can access the DOM to dynamically change the content, structure, and style of a web page
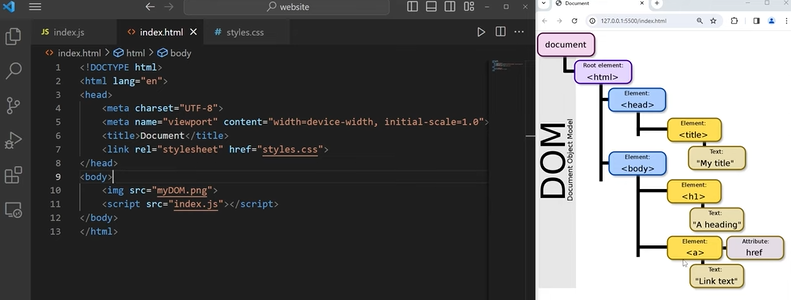
Using JS to manipulate DOM
- the HTML itself represents the initial page content, and the DOM represents the updated page content which was changed by the JavaScript code you wrote
- Objects inside the DOM have property and methods
- properties
- innerHTML
- style
- firstElementChild
- method
- something an object can do (has to be associated with an object unlike a function)
- click()
- appendChild()
- setAttribute()
Examples
document.firstElementChild- gives you
<head>
- gives you
document.lastElementChild- gives you
<body>
- gives you
document.querySelector("input").click()- looks at entire document for the object that has the selector of “input”, then click
- element/class/id
- class:
document.querySelector(".input") - id:
document.querySelector("#title")
- returns 1 item
- selects the first match in the DOM
- looks at entire document for the object that has the selector of “input”, then click
document.querySelectorAll- returns array
document.getElementById("btn")- returns 1 item (not array)
document.getElementsByTagName("li")- looks through the webpage and searches for the elements with a particular tag name
- gets back an array that contains the element
- we can use any methods for the array
- .length
document.getElementsByClassName("btn")- returns array
text manipulation
document.getElementById("btn").innerHTML- gives u the html that’s in between the element tags
"<strong>Hello</strong>"
document.getElementById("btn").textContent- gives you only the string
"Hello"
Attribute manipulation
document.querySelector("a").attributes- gives a list of all attributes
document.querySelector("a").getAttribute("href")document.querySelector("a").setAttribute("href", "the link")- 1st: attribute you wanna change
- 2nd: what you want to change it to
When you’re trying to use JS to change properties instead of CSS
- https://www.w3schools.com/jsref/dom_obj_style.asp
- properties in CSS are hyphen splitted (
font-size) but when it comes to JS, it becomes camel case (fontSize) - but in most cases they are the same
- also the value has to be represented in string (even though its a number)
document.querySelector("h1").style.fontSize = "2rem"
DOM Event types
- User Interface events
- load and unload, abort/error, user selection of text in page
- Focus events
- mouse events
- click, mouseover, etc
- . wheel events
- wheel
- input events
- before/after input
- keyboard events
- composition events
- inputting text in alternate manner