API
- It is the process of verifying the identity of a user or system that is trying to access an API
- It ensures that only authorized users or systems can interact with the API and access sensitive data or perform specific actions
- Need to know who you are
401unauthorized
- Tiers
- No authentication
- Basic authentication
- API Key authorization
- Token based authentication
- Just toy with this w/ postman
No Authentication
- Can prevent abuse (too much requests at the same time) by having a rate limit
- You can check each IP address, how many requests they’re making per minute.
- Common with public APIs
Basic Authentication
- Provide a username and pw when you make an API request to authenticate yourself to an API provider
- Usually done by passing over a Base64 encoded string in the header of the request
- Base64 encoding - converting
username:passwordto bits, then encoding into another character - ex)
jackbauer:ILOVEWEB123!gets encoded and put into header
- Base64 encoding - converting
API Key Authorization
Authorization
- Authentication
- verifying the identity of a user, system, or entity
- confirming that the person or service making a request is who they claim to be
- Authorization
- process of determining what permissions a user, system, or entity has after they are authenticated
- something that allows you to use an API
- API keys
- A lot of public apis use api keys, you can track the usage per key (ex. Google Maps API)
- usually charged for using
Token based Authentication
- We’re getting the user to use a username + password to log in
- Once logged in, we generate a token to be used with the API
- The token is used to interact with the API
OAuth- The industry standard
Example
- diagram
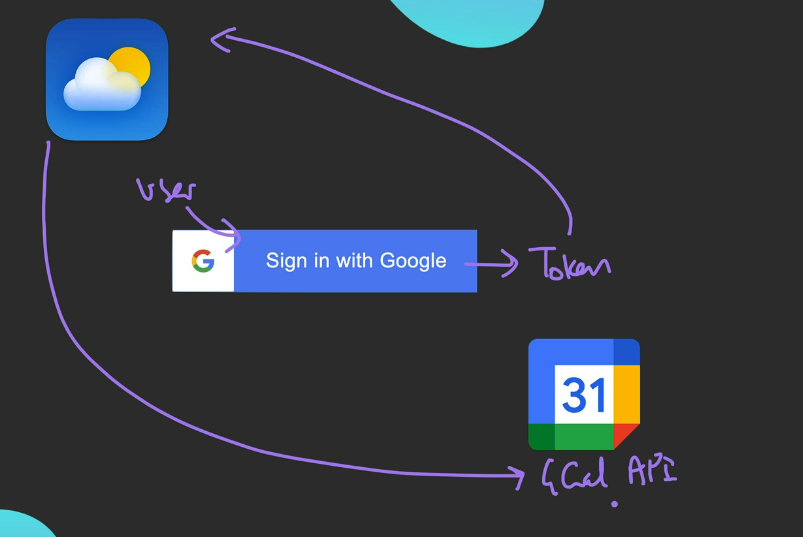
- What’s happening
- “Sign in with Google” generates a token that we can use in our weather app to interact with the google api
- We can maybe get hold of user’s meetings/dates, etc