- Devs mainly do these 2 tasks
- Making programs
- Maintaining programs (유지보수)
- computer networking knowledge is useful for both fields
Basics
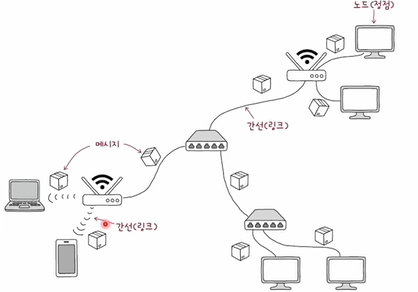
- A network is made out of the hosts (the outermost nodes), network devices (hosts in the middle), communication media (wired/wireless), and the messages
- A network is a graph data structure
- The graph
- Nodes
- Any device connected to a network that can send, receive, or forward data
- includes all hosts and networking devices
- Edges
- Nodes
What’s in a network
- Host
- A host is a device connected to a network that can send and receive data, services, and applications. Examples include computers, laptops, smartphones, servers, and other network-enabled devices.
- Client
- sends request to host
- Server
- sends response to host
- Network devices (네트워크 장비)
- hardware and software that connect devices to a network and allow data to flow between them
- NOT hosts because they don’t directly participate in user applications
- Hub
- Switch
- Router
- communication media (통신메체)
- pathways used to transmit data
- guided/wired
- unguided/wireless
- Message
- The messages/data sent to and from hosts
Switching
Switching is the process of data being transferred from one device to another
- Circuit switching
- Using pre-defined circuits/channels between 2 hosts and using them to send messages
- connection is established before any communication takes place
- no devices are able to use that channel until session is complete
- data travels in the same dedicated path in sequential order
- usually used in telephone systems
- Makes use of a circuit switch
- Using pre-defined circuits/channels between 2 hosts and using them to send messages
- Packet switching
- packet = unit of sending messages
- Payload
- header
- address
- trailer (optional)
- Makes use of a packet switch
- router
- switch
- unlike circuit switching that uses predefined pathways, packet switching is more flexible
- data is broken down into individual packets that take different routes to the destination
- which means data may not arrive in the correct order, but the receiving device will reassemble the packets in the correct order so the data can be read
- Types of ways to send packets
- unicast (1 to 1)
- broadcast - sending the packets to all hosts except itself in the network
- broadcast domain - the range of the broadcast
- packet = unit of sending messages