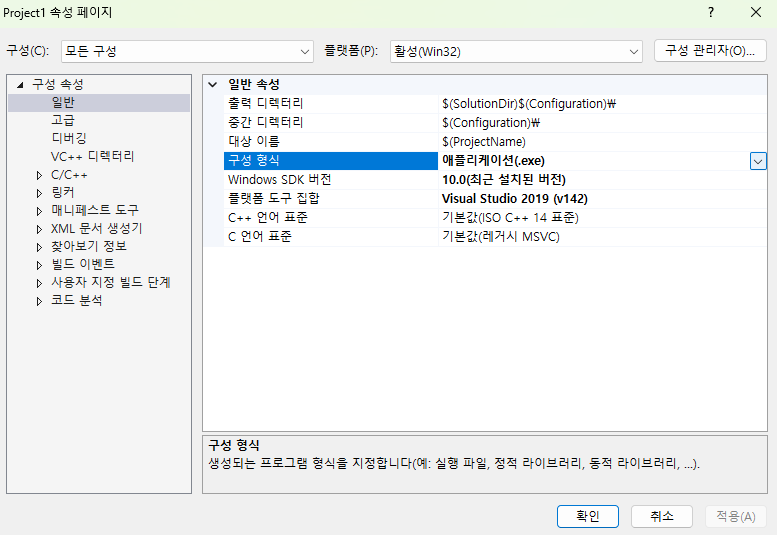
[! C++ is a compiled language.]
- source files (code you write) → compiler “translates” them into machine code (binaries)
- every
.cppfile gets compiled individually into an object file (`.obj)- compile
Ctrl + Shift + B- then the linker takes all the
.objfiles and “glues” them together into one.exefile- then you execute the file via terminal
- C++ comes with an extensive library called the C++ Standard Library (usually called the standard library) that provides a set of useful capabilities in your programs
g++- Both COMPILER AND LINKER
- Output executable w specific name
myprogramg++ file.cpp -o myprogramg++: The C++ compilerfile.cpp: The C++ source file you’re compiling-o myprogram: The name of the output executable (machine code)- g++ takes
file.cppand generates object file (file.o)- contains machine code but not complete executable
- g++ then after compiling, links
file.owith any libraries you may have specified, creating final executablemyprogram(without any extension)- fully linked and complete program
- g++ takes
- So the
g++compiler compiles the source code offile.cppinto an executable object filemyprogram
- Output executable w/o specific name (defaults to
a.out)g++ file.cpp- since there are no
-oflags, the default output file name isa.out(machine code)
- Running the executable
myprogram(ora.out)./myprogram- this executable file will then be loaded o computer memory, and the computer’s CPU will execute the program instruction at a time
Ctrl + Shift + B- Automatically builds for us
Some Visual Code configs
- Solution config and Solution platform
- Solution config - Debug and Release
- Solution platform - x64, x86
- Imp stuff to check