ECS
- Elastic Container/Kubernetes Services
- ECS is AWS’s simpler container orchestrator, letting you define tasks and services without the complexity of Kubernetes.
- EKS is the managed K8s solution, typically more advanced
- All about running containers in the cloud
- diagram
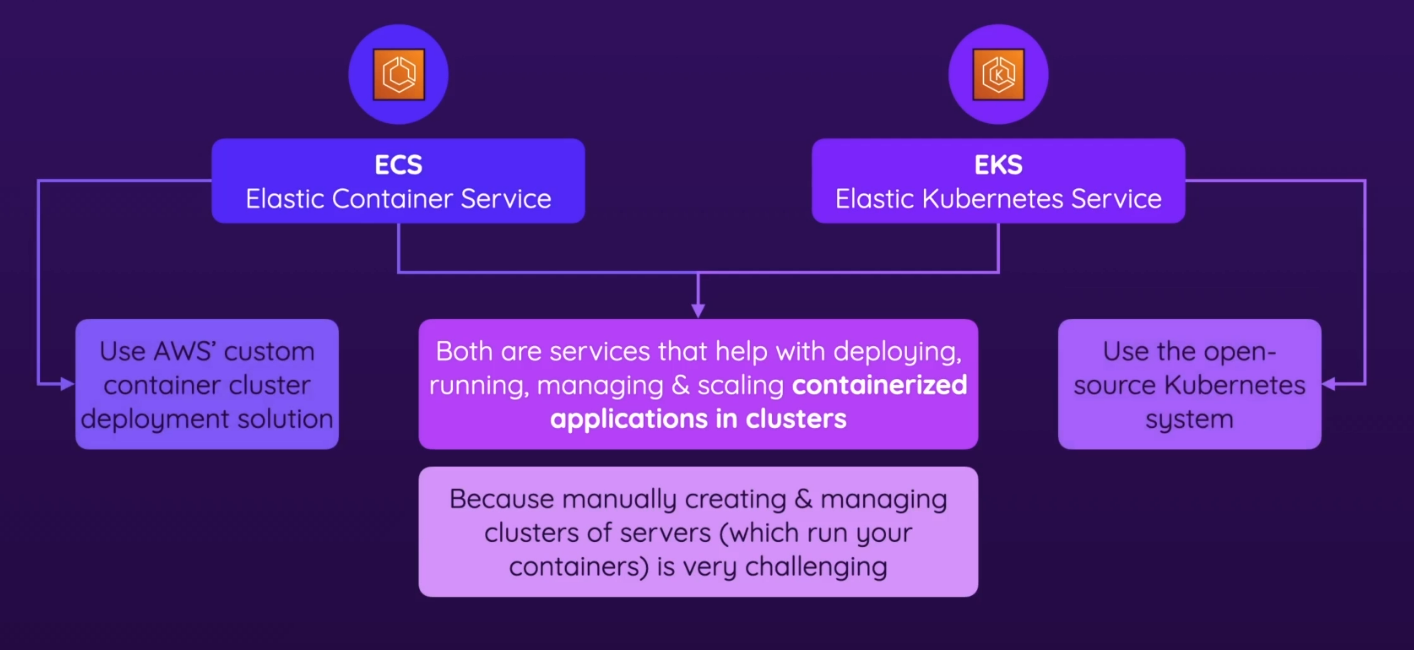
- Services for running containerized workloads on AWS → u want to run images
- Managed container orchestration with many configuration options
- Handles cluster management, container deployment, scaling, and health monitoring
- Alternative to EC2 (not recommended)
- Perfect to fun any kind of containerized workloads
Deeper look
- diagram
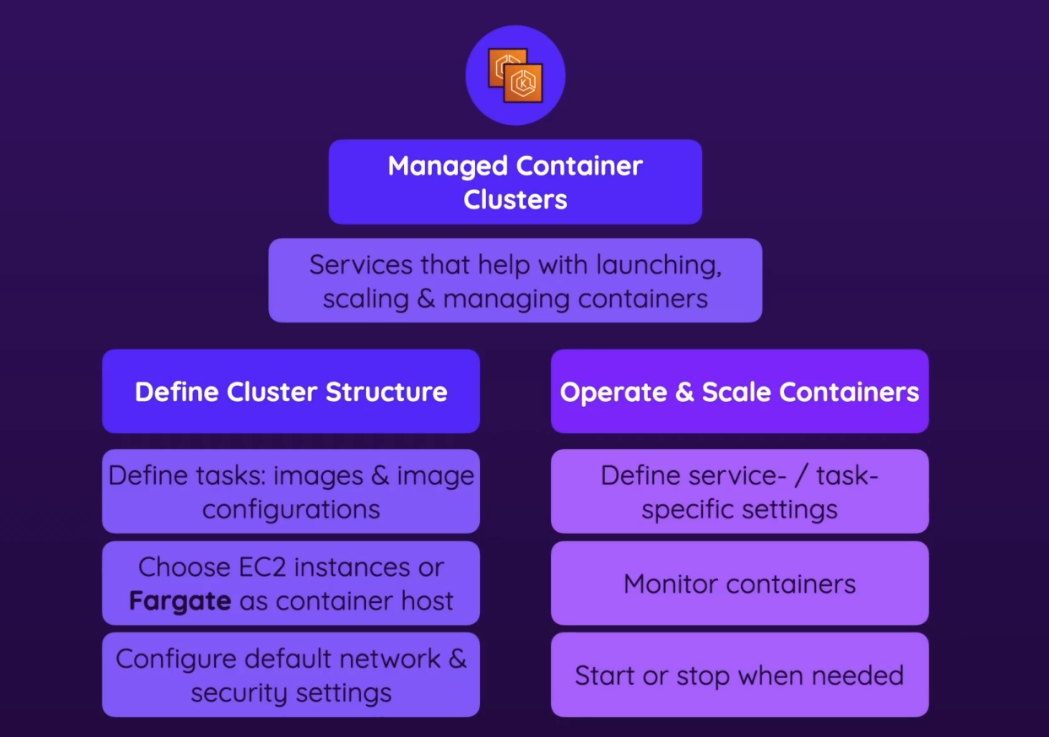
- Define cluster structure
- You have to define your cluster structure = the infrastructure environment where containers run
- Which kind of infrastructure?
- you could use EC2 instances or Fargate as container host
- EC2 instances → these instances will be started and operated by ECS/EKS (and you won’t manage them manually). But you still have to set instance settings when you create a EC2/EKS
- Fargate → recommended
- Tasks: which image you should use & other image configs
- Network & security settings
- Operate & scale containers
- you can define service/task specific settings
- Need to select a Task definitions u want to use first
- service - ongoing task (ex. web servers)
- task - tasks finish at some time
- monitor containers
- stop/start
- schedule tasks (ex. once everyday), or have something running all day (ex. web server)
- you can define service/task specific settings
Task definitions / Task / Service
- A JSON file that describes:
- Which container image(s) to use
- How much CPU and memory to allocate
- Which ports to expose
- What environment variables to set
- How containers should communicate with each other
- Storage volumes to mount
- Network settings
- LIKE A BLUEPRINT
- Task / service
- you can create them by referencing the task definitions you created
- Each cluster can run multiple tasks/services → Tasks/services are at the cluster level
- Task: An instance of a task definition running on your cluster (the actual running containers
- Service: A configuration that maintains a specified number of tasks running at all times (for long-running applications like web servers)
- So when you’re in the AWS Management Console:
- You create task definitions first (the blueprint)
- Then you run tasks or create services based on those task definitions
- Analogy
- Task definition = Recipe
- Task = Meal prepared from that recipe
- Service = Chef who keeps making that meal whenever it’s consumed
Typical workflow
- You build your container image using Docker on your development machine or in a CI/CD pipeline
- You push that image to a container registry like ECR (Elastic Container Registry), Docker Hub, or another registry
- You define how to run your container using:
- ECS: Task definitions and services
- EKS: Kubernetes manifests (deployments, services, etc.)
- ECS/EKS pulls your image from the registry and runs it on the underlying infrastructure
Cluster
ECS/EKS manage clusters of infrastructure (the compute resources)
- A collection of infrastructure resources (servers/compute), managed as a single unit
- Can run many containers across multiple machines
- Provides the environment where containers run
- Handles scheduling, networking, and management
- The relationship w/ containers is hierarchical:
- A cluster contains many nodes (servers/instances)
- Each node can run multiple containers
- The cluster orchestrates how containers are distributed across nodes