What
It is the the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing
- Common cloud services: compute, networking, storage, databases
- diagram
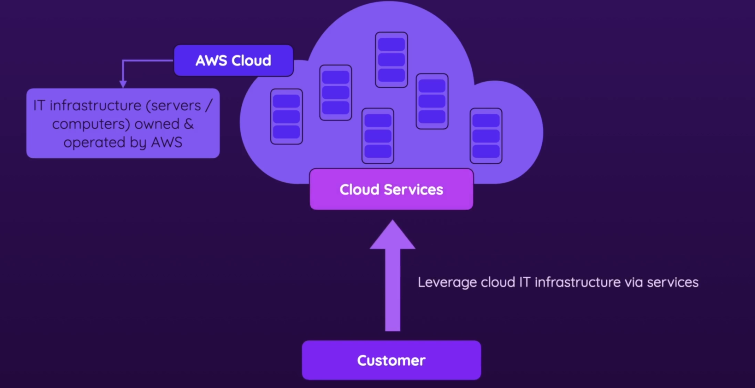
- they own and operate IT resources & infrastructure in their own data centers, that are typically distributed across the entire world
- as a customer, you can use the cloud infrastructure (rent/use IT resources managed by AWS) through cloud services!
- No need to provision/maintain your own data center
Common Cloud Services
- Compute
- Networking
- Storage
- Databases
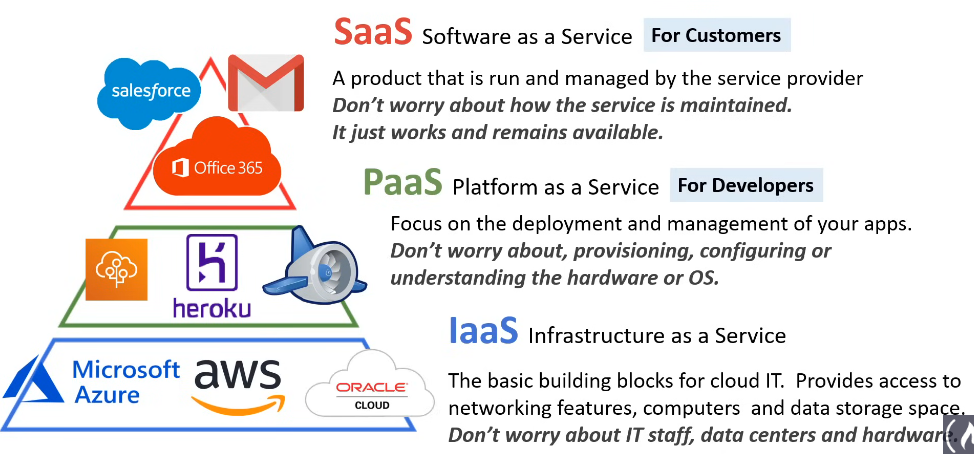
Types of Cloud computing
- diagram
Without cloud computing
- Advantages
- Full control over your physical infrastructure & hardware
- You know exactly where your computers (and data) are
- Disadvantages
- Your responsibility to maintain the infrastructure and protecting it
- Your responsibility for long term capacity planning & upgrading
- Can’t react quickly to workload spikes (ex. more requests)
- Pay for idle resources
- Typically stuck to one or a few locations
Cloud Advantages
- Official source
- Reliability
- Rely on AWS
- AWS operates & maintains the infrastructure (maintenance, capacity planning & upgrades, security)
- Service Level Agreements (SLA) are available for many key services
- Build reliable applications
- Various services help you build reliable applications, correctly & consistently (no matter the circumstances)
- Reliable to keep up with traffic or demand in general
- Rely on AWS Global Reach
- They have data centers all across the globe
- Allows you to fall back to a different region or data center in case
- You can move your workload within mins to hrs (not days/weeks)
- Rely on AWS
- Agility, Elasticity & Scalability
- Agility
- You can use cloud resources within seconds or minutes
- You can configure and start a rented server on which you can install and run any software/workload of your choice in few clicks
- Instant & easy
- Elasticity
- You can start using more/less resources whenever you need to VERY quickly
- No long-term planning required
- Scalability
- Scale up or down as required
- Use auto-scaling services to reduce manual workload
- Agility
- Pay-as-you go
- Generally, you only pay for what you’re using
- If you don’t use it, simply no payment!
- No fixed cost! → You trade fixed expense for variable expense
- No CapEx (capital expenditure) for purchasing/operating your own hardware
- Less OpEx (operating expenditure) since you only pay for service usage, not staff/power
- Benefit from AWS’ economies of scale
- AWS can realize discounts & savings on hardware procurements (+ advantages) which you couldn’t
- Generally, you only pay for what you’re using
- Global Reach & high availability
- AWS own & operate a world-wide network of data centers
- benefit with global reach
- choose a perfect location
- make available/faster to more customers worldwide for high availability
- AWS own & operate a world-wide network of data centers
Cloud Architecture terms
- Availability
- your ability to ensure a service remains highly available
- ensure there is no single point of failure
- Elastic Load Balancer (ELB)
- Scalability
- your ability to grow capacity rapidly or unimpeded
- scaling up (vertical) - upgrading to bigger server
- scaling out (horizontal scaling) - adding more servers of the same size
- Elasticity
- your ability to shrink and grow to meet the demand
- EC2 Auto Scaling
- Fault tolerance
- your ability to prevent failure
- RDS Multi-AZ
- Disaster recovery
- your ability to recover from a failure (highly durable)
- do you have a backup, how fast can you restore the backup, does it work, etc
- CloudEndure Disaster Recovery
- Business Continuity Plan (BCP)